

RADOX-23: The Clear Leader in Air Scrubber Technology
Steen Research holds the exclusive patents on hydroxyl radical generation, RADOX-23, the strongest oxidizer known for use in air scrubbers. Compare the strength of RADOX-23 to the leading super-oxidizers:

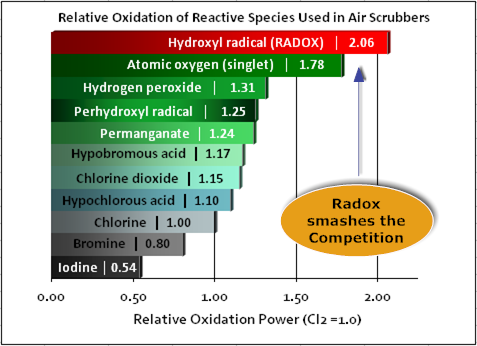
RADOX-23 is proven highly effective in drastically reducing odor emissions and is unmatched in reducing facility operational costs. RADOX-23 utilizes advanced oxidation methodology to eliminate noxious odor-causing compounds, VOCs, and environmentally detrimental by-products such as haloamines and trihalomethanes. RADOX-23 contains state-of-the-art surfactancy and dispersion power to clean and maintain aqueous air scrubber systems.
Abstract From USDA Study
“The RADOX catalyst was shown to be significantly more effective than chlorine dioxide (ClO2) for reducing the concentration of malodorous VOC and total VOC emitted from poultry rendering. Samples from RADOX-treated air streams had (1) a 42±14% (the average plus or minus the standard deviation) higher concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2), (2) 69±9% lower concentrations of the highly aldehyde compounds, and (3) 52±13% lower total VOC when compared to untreated, or ClO2-treated samples. The concentration of highly malodorous aldehyde compounds, which were responsible for a majority of the poultry rendering odor, were not changed by the ClO2 treatment.
Additionally, there was a 5-fold higher concentration of indole in the ClO2 samples when compared to RADOX-treated samples. This is important because indole is a highly odorous metabolite from protein degradation that has an odor threshold of 0.0019 mg/m3 (Zahn et al., 2001). The RADOX treatment reduced the total perceived odor intensity by 74±19%, while the ClO2 treatment did not significantly alter the odor intensity.”
From the USDA study Effect Of A Packed-Bed Scrubber Using Radox Catalyst On The Emission of Odors And Volatile Organic Compounds From A Commercial Poultry Rendering Plant by Zahn et al., 2002
